27/02/2012 14:11:08
The Internet has become part of our everyday lives and is now easier to access then ever before.
Use of the Internet can also have risks. Young people are more at risk of exposure to inappropriate or criminal behaviour if they are unaware of the dangers.
These dangers include:
Don’t arranging to meet an online friend.
Don’t use twitter of any on line chat room.

http://ec.europa.eu/information_society/activities/esafety/index_en.htm
http://www.kent.gov.uk/childrens_social_services/protecting_children/e-safety.aspx
http://www.learningcurve.info/products/e-safety.html
23/02/2012 14:05:31
•1)Howard Carter was born May 9, 1874, in Kensington, London.
•2) His father,Samuel Carter,was a successful artist.
•3) Howard was a sickly child, and was sent to live with his aunts in Norfolk. He had private home schooling, and had an artistic streak from an early age. When his father painted a portrait of a well-known Egyptologist, the young Howard's interest was sparked.

•4) The British had occupied Egypt in the late 19th centry. This period saw an increased European interest in Egyptology, the study of ancient Egypt. Many prominent British scientists and archeologists were active in excavating ancient sites.
•5) Married: Lady Elizabeth Howard, daughter of Thomas Howard, 2nd Duke of Norfolk
•6)Died: 2 March 1939
•7)Character of Howard Carter : Ambitious, autocrat, determined, introvert, perfectionist
•8)Famous for his excavations in Egypt which were 9)financed by Lord Carnarvon and the discovery of 10) the tomb and fabulous treasures of the pharaoh tutankhamun.
•Howard Carter's was 17 when he first went to Egypt.
•12) Over 3,000 treasures were placed in the tomb
•13) In 1891, at the age of 17, a talented young artist, he was sent
08/02/2012 15:55:13
The build up to the 2012 London Olympics provides an excellent hook to engage students all round the world in learning about Britain. I have already written many pages on Britain and will be adding more and linking the resources to the Olympic theme.
The 2012 Summer Olympic Games, officially known as the Games of the XXX Olympiad or "London 2012 Olympic Games", are scheduled to take place in London, England, United Kingdom from 27 July to 12 August 2012.[1] London will become the first city to officially host the modern Olympic Games three times,[2][3] having previously done so in 1908 and in 1948.[4][5]
London was selected as the host city on 6 July 2005 during the 117th IOC Session in Singapore, defeating Moscow, New York City, Madridand Paris after four rounds of voting.[6] The successful bid was headed by former Olympic champion Sebastian Coe.
When will the London Olympics take place?
The 2012 Summer Olympic Games will be held in London from 27 July to 12 August 2012, followed by the 2012 Paralympic Games from 29 August to 9 September.
How many times has London hosted the Olympics?
London hosted the Olympic games in 1908 and 1948.
How many countries are expected to take part in the London 2012 Olympics?
We expect 205 nations to take part in 300 events at the Olympic Games in 2012. 147 nations will take part in the Paralympic Games.

The Olympic Rings are five interlocking rings that stand for the five original continents, (Africa, America, Asia, Australia, and Europe) and the athletes from around the world.
The colours of the rings are blue, yellow, black, green, and red respectively. They were chosen because at least one of these colours is found on the flag of every nation.

On the Olympic flag, the rings appear on a white background.
At the Olympic Games, the flag is brought into the stadium during the opening ceremony. After its arrival, the flag is hoisted up the flagpole. It must fly in the stadium during the whole of the Games. When the flag is lowered at the closing ceremony, it signals the end of the Games.
The 26 Olympic sports at London 2012 will be:
- Aquatics
- Archery
- Athletics
- Badminton
- Basketball
- Boxing
- Canoe and Kayak
- Cycling
- Equestrian
- Fencing
- Football
- Gymnastics
- Handball
- Hockey
- Judo
- Modern Pentathlon
- Rowing
- Sailing
- Shooting
- Table Tennis
- Taekwondo
- Tennis
- Triathlon
- Volleyball
- Weightlifting
- Wrestling



more info to come when it starts!
07/02/2012 16:20:53
http://www.porsche.com/uk/
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K1rCLkyG-F0
he Porsche 944 is a sports car built by Porsche from 1982 to 1991. It was built on the same platform as the 924, although 924 production continued through 1988. The 944 was intended to last into the 1990s, but major revisions planned for a 944 S3 model were eventually rolled into the 968 instead, which replaced the 944. The 944 was a successful model and was available as both a coupe and cabriolet in naturally aspirated and turbocharged forms.
944 Turbo (951/952)
For the 1986 model year Porsche introduced the 944 Turbo, known internally as the 951 (952 for right-hand drive models). This had a turbocharged and intercooled version of the standard car's engine that produced 220 hp (164 kW) (217 hp (162 kW) in the US) at 6000 rpm. The turbo was the world's first car using a ceramic portliner to retain exhaust gas temperature. The Turbo also featured several other changes, such as improved aerodynamics, a strengthened gearbox with a different final drive ratio, standard external oil coolers for both the engine and transmission, standard 16 inch wheels (optional forged Fuchs wheels), and a slightly stiffer suspension to handle the extra weight. Major engine component revisions, more than thirty in all, were made to the 951 to compensate for increased internal loads and heat.

1987 Porsche 944 Turbo (US Model)
Few changes occurred for the 1987 model year. They included the deletion of the transmission oil cooler, a change in suspension control arms in order to reduce the car's scrub radius, and for the first time ever offered in a production car, standard dual airbags. The engine remained the same M44/51 powerplant as in the 1986 model. In 1988, Porsche introduced the Turbo S option package (SE in the UK). The 944 Turbo S had a more powerful engine (designation number M44/52) with 250 hp (186 kW) and 250 lb·ft (340 N·m) torque (standard 944 Turbo 217 hp (162 kW) and 243 lb·ft (329 N·m)). This higher output was achieved by using a larger #8 turbine housing and revised engine mapping which allowed for slightly more boost at high rpms as compared to the standard Turbo. In June 1988, Car and Driver tested the 944 Turbo S and achieved a 0-60 mph time of 5.5 seconds and a quarter-mile time of 13.9 seconds at 101 mph (163 km/h). Top speed was factory rated at 162 mph (261 km/h).
The 944 Turbo S's suspension was the then state-of-the-art "M030" option consisting of Koni adjustable shocks front and rear, with ride height adjusting threaded collars on the front struts, progressive rate springs, larger rear torsion bars, harder durometer suspension bushings throughout, larger 26.8 mm (1.1 in) anti-roll bars at the front, and chassis stiffening brackets in the front frame rails. The air conditioning dryer lines are routed differently to clear the front frame brace on the driver's side. The 944 Turbo S wheels, known as the Club Sport design, were 16-inch forged and flat-dished, similar to the Design 90 wheel. Wheel widths were 7 inches (178 mm) in the front, and 9 inches (229 mm) in the rear; sizes of the Z-rated tires were 225/50 in the front and 245/45 in the rear. The front and rear fender edges were rolled to accommodate the larger wheels. The manual transmission (case code designation: AOR) of the 944 Turbo S brought back the external cooler, and also featured a limited slip differential with a 40% lockup setting. The Turbo S front brakes were borrowed from the Porsche 928 S4, with larger 4-piston fixed calipers and discs; rear brakes remained the same as a standard Turbo. ABS also came standard.
The 944 Turbo S interior featured full power seats for both driver and passenger, where the majority of the factory-built Turbo S models sported a "Burgundy plaid" (Silver Rose edition) but other interior/exterior colors were available. A 10-speaker sound system and equalizer + amp was a common option.
In 1989 the 'S' designation was dropped from the 944 Turbo S, and all 944 Turbos featured the 'S' package as standard.


05/02/2012 16:48:21

The new win 8
BAD
the colours were designed by someone who was colour-blind!!

GOOD
It has an app store with cut rope and driving game like jelly cor on iphone and ipod touch.
It was released on the 28th of febuary.
05/02/2012 16:04:48
Red Bull-Renault
Race drivers
1. Sebastian Vettel (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
2. Mark Webber (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Daniel Ricciardo (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
McLaren-Mercedes
Race drivers
3. Lewis Hamilton (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
4. Jenson Button (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Gary Paffett (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Pedro de la Rosa (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Ferrari
Race drivers
5. Fernando Alonso (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
6. Felipe Massa (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Jules Bianchi (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Giancarlo Fisichella (2010 driver) | biography | articles
Marc Gené (2010 driver) | biography | articles
Mercedes
Race drivers
7. Michael Schumacher (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
8. Nico Rosberg (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
TBC
Renault
Race drivers
9. Nick Heidfeld (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
10. Vitaly Petrov (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Bruno Senna (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Romain Grosjean (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Fairuz Fauzy (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Jan Charouz (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Ho-Pin Tung (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Williams-Cosworth
Race drivers
11. Rubens Barrichello (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
12. Pastor Maldonado (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Valltteri Bottas (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Force India-Mercedes
Race drivers
14. Adrian Sutil (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
15. Paul di Resta (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
NB. The number 13 is not used on Formula 1 cars. See here for more information.
Test drivers
Nico Hülkenberg (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Sauber-Ferrari
Race drivers
16. Kamui Kobayashi (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
17. Sergio Perez (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Esteban Gutierrez (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Toro Rosso-Ferrari
Race drivers
18. Sebastien Buemi (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
19. Jaime Alguersuari (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Daniel Ricciardo (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Lotus-Renault
Race drivers
20. Heikki Kovalainen (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
21. Jarno Trulli (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Karun Chandhok (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Luiz Razia (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Davide Valsecchi (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Ricardo Teixeira (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
HRT-Cosworth
Race drivers
22. Narain Karthikeyan (rounds 1-8) | biography | articles
22. Daniel Ricciardo (round 9-) | biography | articles
23. Vitantonio Liuzzi (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
TBC
Virgin-Cosworth
Race drivers
24. Timo Glock (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
25. Jerome d’Ambrosio (has 2011 contract) | biography | articles
Test drivers
Sakon Yamamoto (rounds 1-3) | biography | articles
Robert Wickens (round 7-) | biography | articles


05/02/2012 15:02:52

above is the famous Jonny Wilkinson.
He now only plays club rugby
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Six_Nations_Championship
this has all the details of the famous tournament

Rugby At The Beginning
04/02/2012 19:25:18

first plane

hippo

canopic jars

tiger

ocelot
mirror

sarcophagus
02/02/2012 12:42:01
Sobek (also called Sebek, Sochet, Sobk, Sobki, Soknopais), and in Greek, Suchos (Σοῦχος) was the deification of crocodiles, as crocodiles were deeply feared in the nation so dependent on the Nile River. Egyptians who worked or travelled on the Nile hoped that if they prayed to Sobek, the crocodile/Nile god, he would protect them from being attacked by crocodiles.[1] The god Sobek, which was depicted as a crocodile or a man with the head of a crocodile was a powerful and frightening deity; in some Egyptian creation myths, it was Sobek who first came out of the waters of chaos to create the world.[1] As a creator god, he was occasionally linked with the sun god Ra.[1]

Pharaoh Amenhotep III and god Sobek

Sobek in crocodile form, 12th Dynasty (Staatliches Museum Ägyptischer Kunst, Munich)
During the twelfth and thirteenth dynasties (1991 BC - 1650 BC), the cult of Sobek was given particular prominence and a number of rulers incorporated him in their coronation names.[2] Most of Sobek's temples were located "in parts of Egypt where crocodiles were common."[1] Sobek's cult originally flourished around Al Fayyum where some temples still remain. The area was so closely associated with Sobek that Arsinoe was known to the Greeks as Crocodilopolis or 'crocodile Town.'[1] Another major cult centre was at Kom Ombo, "close to the sandbanks of the Nile where crocodiles would often bask.[1] Some temples of Sobek kept pools where sacred crocodiles were kept: these crocodiles were fed the best cuts of meat and became quite tame.[1] When they died, they were mummified and buried in special animal cemeteries. In other areas of Egypt, however, crocodiles were dealt with by simply hunting and killing them.
Gradually, Sobek also came to symbolize the produce of the Nile and the fertility that it brought to the land; its status thus became more ambiguous.[3] Sometimes the ferocity of a crocodiles was seen in a positive light, Sobek in these circumstances was considered the army's patron, as a representation of strength and power.
In Egyptian art, Sobek was depicted as an ordinary crocodile, or as a man with the head of a crocodile. When considered a patron of the pharaoh's army, he was shown with the symbol of royal authority - the uraeus. He was also shown with an ankh, representing his ability to undo evil and so cure ills. Once he had become Sobek-Ra, he was also shown with a sun-disc over his head, as Ra was a sun god.
In other myths, which appeared extremely late in ancient Egyptian history, Sobek was credited for catching the Four sons of Horus in a net as they emerged from the waters of the Nile in a lotus blossom. This motif derives from the birth of Ra in the Ogdoad cosmogony, and the idea that as a crocodile, Sobek is the best suited to collecting items upon the Nile.
01/02/2012 17:17:15
7 points
26.63 fastest time ever!
place 15
9 points
fastest lap 27.16
place 15th
points 6
fastest time 27.79
condition dry
place 15
POINTS 7
fastest lap 0.40s
place 15 out of 28
bad car!!
01/02/2012 16:21:12
pics for school
    


imsety
In Egyptian mythology, Imseti (also transcribed Imset, Amset, sety, Mesti, and Mesta) was a funerary deity, one of the Four sons of Horus, who were associated with the canopic jars, specifically the one which contained the liver. Unlike his brothers, Imsety was not associated with any animal and was always depicted as human. The early form of Isis was considered his protector.
Imsety is one of the four sons of Horus, he was portrayed as a mummified human.
Horus (the elder) had numerous wives and children, and his 'four sons' were grouped together and generally said to be born of Isis. Imsety was one. The other three were Duamutef, Hapyand Qebehsenuef. They were born from a lotus flower and were solar gods associated with the creation. They were retrieved from the waters of Nun by Sobek on the orders of Re. It was believed that Anubis gave them the funerary duties of mummification, the Opening of the Mouth, the burial of Osiris and all men. Horus later made them protectors of the four cardinal points (north, south, east and west). In the Hall of Ma'at they sat on a lotus flower in front of Osiris. Most commonly, however, they were remembered as the protectors of the internal organs of the deceased. Each son protected an organ, and each son was protected by a goddess.
Imsety's role was to protect the liver of the deceased and was the guardian of the South. He was protected by the goddess Isis.
imsety

all agyption gods
Ancient Egypt had by tradition a great variety of gods and what today can be labeled as spirits and divine forces. Some were depicted just as symbols and others had the form of living createures.
In total they were over 2.000(!) but many had similar characteristics and appeared all over the country but with different names. This great diversity is due to the fact that before the country was united the northern Nile Valley was split up into about forty self ruling areas (later to be provinces - called nomes) where the ruling tribes had their own deities and leaders.
From the dualism of all gods it's clear that animals were the first to get divine status and by time got human form.
Because of this all gods had two things in common - they were family members with counterparts from the opposite sex and manifested them- selves on earth through animals.
Thus the local wild fauna of birds, crocodiles, snakes, turtles, frogs, plus cattle, dogs, cats and other domesticated animals were considered to be the living images of a particular god or goddess and a natural and indestructible part of the environment in which people lived.
All parts of life were covered and there were gods for - beer, plants, digestion, the high seas, female sexuality, gardens, partying etc. Many of them had lots of duties and were with time combined with each other in a great number of ways.
Some of them could appear in rather unusual forms like a goddess (curious even by Egyptian standards) having a head of a bee and body from a hippopotamus.
When having a glance at a depiction of them shown in upright position with human bodies, the goddesses are easy to single out since they always had their legs joined together, while the males used to be seen on the move - striding.
 Taueret Taueret |
Different towns struggled to have just their local gods at top of the state religion and thus we have many different religious legends over the years depending upon which town had the greatest politi-cal influence during the period. To increase the number of sup-porters nation wide they could "borrow" abilities from popular gods and give to their own. Because of this over the years different gods came into fashion and later went out of style, with exception of a group that was in front right from the beginning and never lost its popularity. These were responsible for basic and vital things in life like love, joy, dancing, childbirth, justice, and life after death.
All aspect of daily life were covered by at least one of these deities, and like people on earth a vast majority of them were married (of- ten to their siblings) and had children.
Many ingredients made it possible for common people to identify themselves with them since their personalities were made of both divine strength and human weakness. They did most of the things that ordinary people did, like harvesting, hunting, eating, drinking, partying and even dying. Most of them were depicted as men and women combined with the head of the animal by which they were represented and they could appear in different costumes and be represented by several animals in the Egyptian fauna.
In other words - they could appear in many ways and yet some of them were so alike looking that it's impossible to identify them without reading the connecting text. Just looking at the dresses and the regalia they carry along isn't always enough, because they used to borrow objects from each other. This guesswork is a part of the charm when looking in to their in many ways, to us, unlikely world.
As to their names, today we use a blend of both their original Egyptian ones like Re, Ptah and Amon, and the Greek forms like Isis, Osiris and Horus.
Shrines
As for the veneration of the gods scholars of Egyptology doesn't know exactly how this was made during the oldest times, or at what point in history the main gods had cult areas replaced by temples of their own.
One clue might be the god Min (see him) who obviously had a very old cult at Koptos in Upper Egypt where two statues of him larger then life size were found in the late 1800s. They had no doubt been situated within a sacred area or by a shrine of some sort, but no remains are left to reconstruct what it may have looked like.
After the formation of two separate countries along the Nile (Upper and Lower Egypt) a typical building came to be in each part, which more or less symbolized the country itself in both a religious and political way and underlined its national identity.
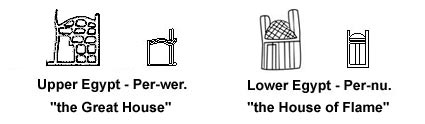 |
It's most likely that local temples made of clay and reed originally were the cult buildings used by tribes along the Nile, and with time two shrines were specified where people could make offers to the main gods. Through their different designs it's easy locate the origin of old writings found since their depictions were incorporated into the hieroglyphic signs at an early stage (shown to the right of each illustration above).
Per-wer, meaning "the Great House", stood for Upper Egypt, and Per-nu, "the House of Flame" was the cupola shaped roofed national temple of Lower Egypt.
They are both attested for already during the reign of pharaoh Aha at the beginning of the first dynasty where they are present on a famous wooden label.
If at this stage, all mayor gods were worshipped in these buildings is not known.
With time the temples were elaborated to be great stone building just for a few very popular gods and goddesses which had fame over the centuries throughout the long Egyptian history. Minor gods had small shrines or were venerated in the homes.
Clothing
When the goddesses and gods were depicted with a human body the variety wasn't so big in the way they were dressed. Less then half a dozen types of garments covers almost all of them. From the beginning they all wore white dresses, or at least single colored. This tradition slowly changed over the years and with time the colors and patterns became elaborated. The peak was reached during the Greco-Roman period when they were seen in outfits like actors in a costume spectacle in a theatre.
Excluding the mummy-like creations, here is a type description in brief:
 |
- Tunic with suspenders.
Male garment, ending above the waist
and popular in all times. Example:Re.
- Dress with suspenders.
Female garment, ended above the waist,
and was usually white. Example:Hathor.
- The short loincloth
Short and skirt-like garment and popular from earliest times. Example: Asar-hap.
- The short-sleeved overall
From the earliest times very common
tight female garment. Example:Isis.
- The full-length dress
Unusual, sleeve-less and for goddesses.
Went up to the neck. Example:Seshat.
|
 |
Notice that long sleeves were not in fashion in any era of Egyptian history, at least for the gods and goddesses. Their dresses were to a great extent similar to those worn by the upper classes in society during daytime and evenings, and mostly indoors.
Pharaoh's crown
The gods had a lot of different things to put on their heads, and they surely did. In bright contrast to the stereotyped positions of their bodies the painters and sculptors were keen on giving the heads as much attention as possible. This was obviously initiated by pharaoh himself or the priesthood in order to give their favorite gods as much promotion as possible. The different crowns could give a hint where the god originally came from, and by wearing the combined crown for the whole country, the message was given that this god or goddess was important to all Egyptians. To make them conspicuous all crowns, hats etc. were adorned with plumes, horns, snakes, flowers, sun discs, leaves etc painted in bright colors. Especially during the Greco-Roman era the fantasy and elaboration was significant.
 |
| Deshret Hedjet Peshent Peshent Atef Atef with horns Khepresh |
|
EGYPTIAN CROWNS: The red one was from Lower and the white from Upper Egypt.
The double crown represented the whole country. The Atef-crown was worn by Osiris and the type with horns and the sun disc by Re-Horakhte and other gods. The blue helmet-like came during dynasty 18 and was worn by kings and the god Amon.
|
Headgears of the gods
Besides royal crowns the gods had a lot of other symbols and things to wear upon their heads. In some cases the headgear was necessary to identify the deities in ques-tion, when they were dressed the same, as they often were. Here is a selection of per-sonal things helping to identify which goddess is depicted in case the written hiero-glyphs don't give a clue. The following objects below are shown as they looked when the bearer in question was facing right.
Neit had the a stylised form of her shield and crossed arrows on her head. Isis wore a throne on top, a rather uncomfortable one it seems, and Maát had her standing ostrich feather she was named after. Nephtys had a building topped with a bowl-like object (for collecting rain water?) and Nut had a pot (or a broad vase) upon her head.
Selkhet wore the dangerous scorpion (without its deadly sting), and Seshat had the holy Persea-tree with two horns over it as her personal sign. Anat had a stylized cow's uterus as her token.Hathor had several objects in her hat box like cow's horns with the sun disc and her favorite musical instrument - the sistrum, which was a rattle.



  

|
|